Table of Contents
Where Buildings Inspire Innovation and Growth
Join us in creating spaces where sustainability, technology, and humanity intersect, turning buildings into platforms for innovation and growth.
Introduction
With the rise in Internet of Things (IoT) device connections over the years, not only are devices getting smarter and more connected, even the buildings that we occupy are becoming smarter too. Even as the concept of smart buildings grows more prevalent, according to the Continental Automated Buildings Association (CABA), unlike green buildings, smart buildings are currently not evaluated based on a specific set of ratings or criteria. Furthermore, with constantly evolving technology and changes in societal trends or needs, features of smart buildings tend to be subjective. So how do we know if a particular building is ‘smart’ and what makes it so?
Fortunately, studying existing smart buildings can help us to understand critical features that define what makes a building ‘smart.’ As suggested by the CABA, smart buildings can be evaluated based on innovation in these key areas – Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning (HVAC) control, office design, and data analytics around occupancy and energy efficiency, to name a few.
Let’s explore 6 leading examples of smart buildings to help us understand some key features of what makes buildings ‘smart.’
Fulton East (Chicago)

The Fulton East is a 12 storey office and retail building that has incorporated futuristic innovations to address the reality of health and safety concerns that arose from the pandemic, given that a clean and well-sanitized environment is crucial in helping to prevent the spread of viruses. The building has an air purification system, microbicidal interior latex painted walls and foot-activated elevator call buttons. These features contribute to a safer working environment that is driven to eliminate and reduce the risk of bacteria and viral transmissions from person to person.
The Crystal (London)
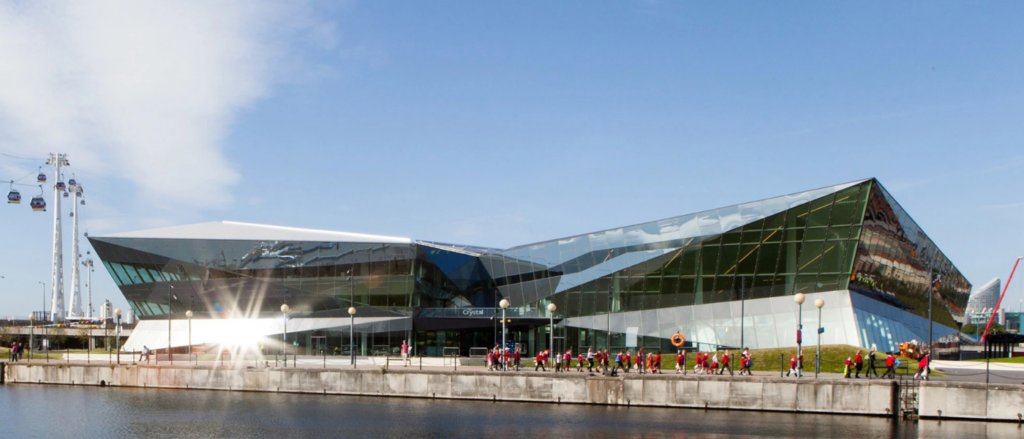

Operating as one of the world’s most sustainable buildings that is fully electric, The Crystal has solar roof panels which supply about 20% of its power. Depending on the time of day and the level of occupancy, the lighting system is automatically adjusted for energy conservation. This building also utilises data collected from over 3,500 data points based on IoT devices and sensors that extensively monitor energy consumption. Given these features, The Crystal has successfully achieved a carbon emission rate that is 70% lower than other buildings.
The Edge (Amsterdam)
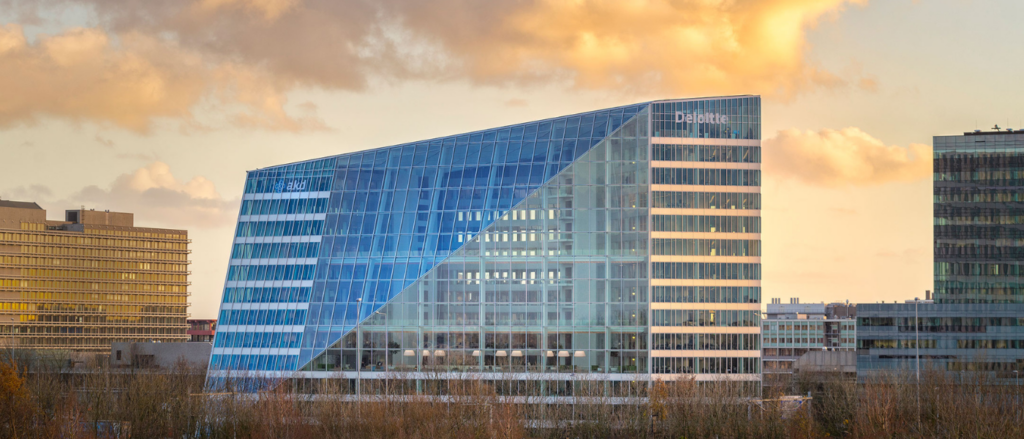

According to a British rating agency BREEAM, The Edge is the most intelligent building in the world. A unique feature of The Edge is its use of Power over Ethernet (PoE) LED light panels which carry both data and power for the building’s operations based on motion, light, temperature, humidity and infrared sensors. This helps the building to track and manage energy consumption efficiently. Further, based on a smart app with data on employees’ schedules, each employee is assigned to a workspace that is most favorable to his/ her schedule and tasks for the day. Thereafter, employees can adjust the lighting and temperature of their workspace according to their preferences. Interestingly, the building can even recognise employee’s cars and direct them to parking spots.
Capital Tower (Singapore)
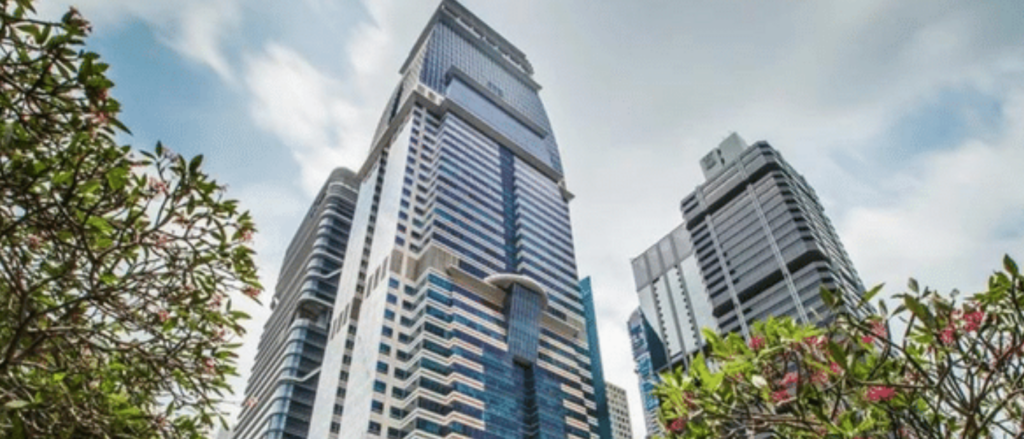

Besides providing a panoramic view of Singapore’s skyline, this 52 storey building has been awarded the Green Mark Platinum status by the Building and Construction Authority (BCA) of Singapore. The Capital Tower utilizes a smart energy system which includes motion sensors in the lobby and bathrooms to conserve energy, and an air conditioning energy recovery system that is able to retrieve cold air and draw on condensation from the air handling unit to reduce water usage.
Burj Khalifa (Dubai)
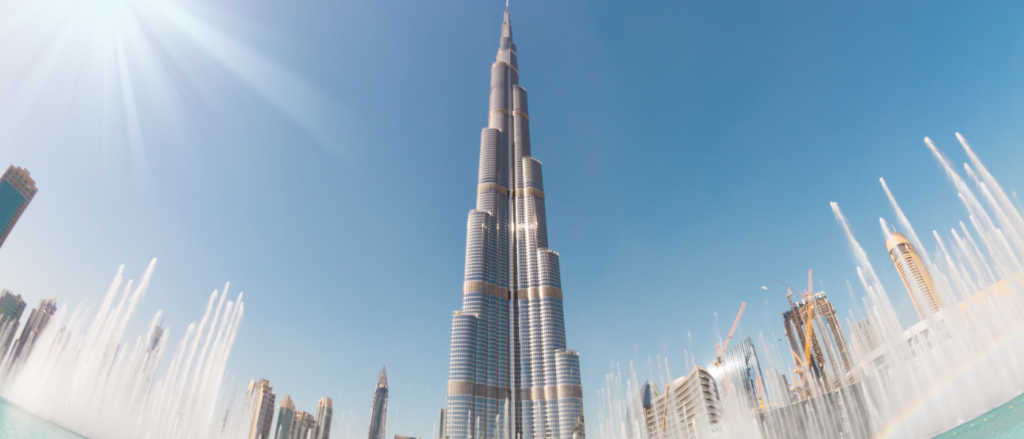

Standing at 2,716 feet tall, this 160 storey building is the tallest building in the world. Additionally, this building also prides itself in being ‘smart’ by utilising IoT devices, sensors and software to monitor, analyze and utilise data to enhance the building’s performance. The Burj’s building management system is able to relay real time information to their IoT platform and efficiently identify when and where building maintenance is required. With the technology that facilitates a predictive maintenance system, building maintenance and asset reliability of the Burj is enhanced as the number of unplanned reactive maintenance is significantly reduced.
JTC CleanTech (Singapore)
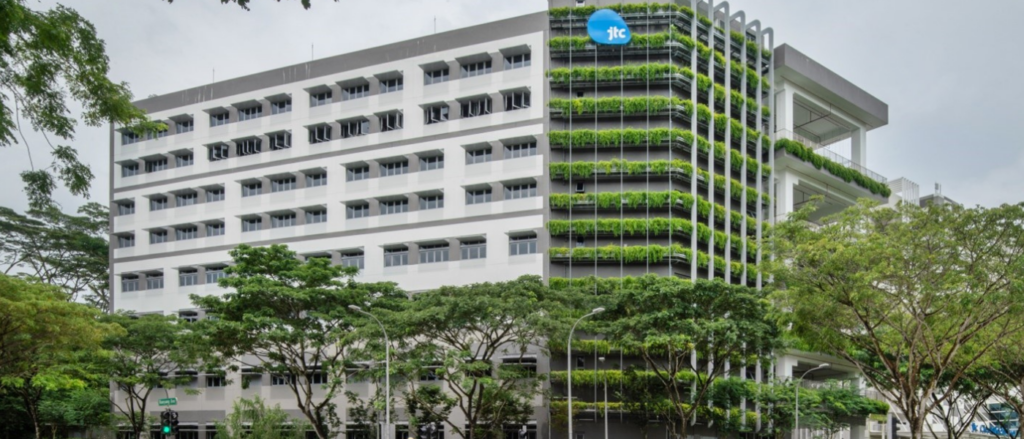

CleanTech One is Singapore’s first eco-business park, well-known by corporations that value sustainability goals. A particular noteworthy feature of the building is its wastewater treatment system, which recycles water for varied purposes such as toilet flushing, cooling towers and landscaping. This endeavour also minimises the amount of sewage waste into the sewage network. Another feature of this smart building is its use of solar energy to power corridor lighting, lifts, and car parks. Additionally, one of CleanTech One’s tenants, Ecolabs, employs Resync’s Intelligent Energy Management solution to monitor and forecast energy consumption, optimise energy usage, and provide advanced data analytics.
With further advances in smart building technology, we can expect a wider range of innovations that serve to enhance a building’s functionality in accordance with the needs of occupants, the society and environment. Based on the innovative features of smart buildings indicated above, we can also conclude a definitive pattern between them – a sense of value towards utilising clean and green technology, contributing towards a more sustainable future. A smart building is strongly tied to the idea of a green building, with emphasis on the use of solar power technology, water treatment systems, air purification systems and building management systems for optimal energy management, and so on.
References:
Contact Us:
Our website: www.resynctech.com
For Enquiries: info@resynctech.com
Where Buildings Inspire Innovation and Growth
Join us in creating spaces where sustainability, technology, and humanity intersect, turning buildings into platforms for innovation and growth.